Coaxial cables are commonly employed by cable operators phone companies, cable operators, as well as internet service providers around the world to transmit video, data and voice messages to their customers. It is also used extensively in homes.
The coaxial cable was in use for quite a while as a method of transmission (since the beginning of the twentieth century) and offers a variety of unique advantages that ensure reliable, precise transmission.
It also has some limitations which could cause its replacement in certain instances with fiber optic cable, category cable, or sometimes it is replaced with wireless signal.
The secret to Coaxial Speaker Cable popularity is its shielded design. This lets the core copper of the cable to quickly transmit data without being subject to environmental or physical damage due to elements.
Table of Contents
The Two Most Common Cable Sizes are RG-6 and RG-11:
- RG means “radio grade”, they are also referred to as RF cables, which is “radio frequency”.
- The RG-6 cable is utilized to connect drops that are less than 150 feet.
- The RG-11 cable is commonly used for longer drops because of the improved performance for lengths of more than 150 feet.
- Broadband cables that are used in homes are 75 Ohms.
Drop cables made of Coaxial Speaker Cable are typically terminated using connectors that conform for the F-type interface as specified by SCTE. Through time, the F-type interface technology has advanced significantly which has led to a variety of termination methods, including crimp screw-on and compression.
To connect to make a connection, a male and female connector that are of the same design is required. Male connectors feature a central conductor or pin that protrudes dependent on the drop cable type and female connectors feature an receptacle to hold the pin or center conductor to connect to.
In the event of incorrect termination tools, damaged materials or connections that are loose It is important to be aware of the result could result in signals entering or exiting. This can result in tiling or signal distortion or even complete signal loss.
THE IMPORTANCE OF QUALITY TESTING OF COAXIAL CABLE
What is Coaxial Cable?
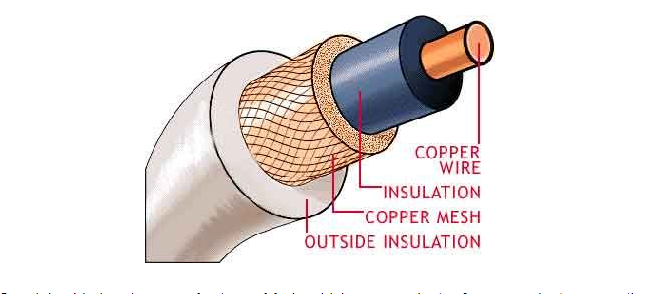
Coaxial cable is a kind of cable with an inner conductor that is surrounded by an insulating coating, which is surrounded by shielding conductive (outer conductor) and an outer jacket. The following diagram illustrates the basic structure of the typical cable. The electrical signal is carried by the conductor in the middle.
1. Center conductor – steel with copper-clad.
2. Clean stripping polymer is used to stop the movement of moisture.
3. Dielectric Polyethylene closed-cell foam that has high VP that provides mechanical stability.
4. First outer conductor – an aluminum-polymer-aluminum tape securely bonded to the dielectric.
5. A second conductor outside – one that is a 34 or 36 AWG aluminum braid
6. Third outer conductor – an additional aluminum-polymer-aluminum tape is used in tri-shield and quad-shield constructions to further enhance HF shield isolation before and after flexure.
7. Fourth conductor outer (optional) An additional 33 or 36 AWG aluminum braid can be used in quad-shield designs to enhance LF shielding in the most extreme areas of RF noise.
Corrosion resistant protectant
- indoor and air is a non-drip substance that is designed to stop corrosion of metallic parts that make up the cables.
- Underground is a compound that flows capable of preventing the movement of moisture.
Jacket Jacket – a UV stabile outer shell made of the polyethylene (PE) or polyvinylchloride (PVC) which is a flame retardant (PVC) to safeguard the cable’s core throughout the lifetime of the cable.
10. Integral messenger is an electro-galvanized carbon steel wire support member that is attached to the cable with separable web.
Which Is Better: Coaxial Cable or Fiber Optic Cable?
Both kinds of cables can be used to carry audio, video and various other kinds of data. Both provide certain advantages, as well as drawbacks when creating your network.
The best choice for you is dependent on the distance you connect to as well as the volume of data that you will transmit. Cables with fiber optic connections provide a signal for several miles prior to having to use repeaters. The signal loss is higher with coax cables, which is why you should choose it for smaller distances. Fiber optic cables transmit more data, and is also more costly. Fiber optic cables are used more rarely in the consumer and residential setting than coaxial cables. However, fiber networks continue to expand throughout the world.
Coax cables are straightforward to set up and are extremely robust. Since fiber provides superior and speedier data transfer rates than coax which is why they are preferred for professional networks and multi-dwelling unit (MDUs) like those that are found on a commercial campus and university or apartments. If you’re conducting a home installation or a medium-capacity data transfer network, the majority of people prefer to use coax cables.
Most companies of today utilize cables to provide their pakistan toy shop for business. Cable internet’s main drawback is its speed fluctuations. In comparison to fiber internet as compared to. broadband internet via cable, the cable internet is typically distributed among many customers. That means that if there’s several subscribers in a particular region that are all using bandwidth-intensive programs on the internet simultaneously and everyone’s speed can fluctuate between 25 and 100 percent of the speed promised.
Concerning the price of fiber as compared to. coax the latter is usually more expensive initially, but has a longer life. Following installation, the cost for internet access that is dedicated over fiber is also higher than the cost of a shared cable internet connection. It’s crucial to weigh your possibilities before making this important decision , which will affect your network’s service in the near future.